The recent Europe cyber attack by Russian hackers has raised significant concerns in cybersecurity communities worldwide. Reports reveal that HeadLace malware is at the center of this cybersecurity threat, primarily aiming to steal valuable data. The software represents major hazards to governments, businesses, and individuals using it to steal credentials throughout Europe. In order to safeguard future European information theft situations, this piece explores the specifics of the HeadLace cybersecurity attack, its possible effects, and the actions taken by governments and cybersecurity professionals.
Understanding HeadLace Malware: A New Cybersecurity Threat
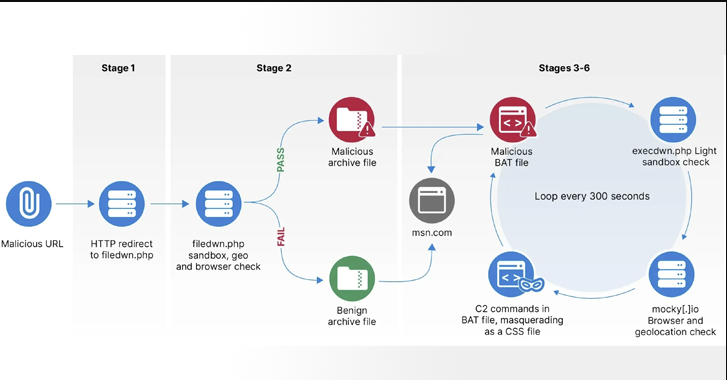
HeadLace malware has quickly become one of the latest cybersecurity threats impacting Europe. This virus is a component of a fresh wave of assaults made with credential harvesting in mind. Targeting usernames, passwords, and other private data kept on computers and mobile devices, it breaches systems. Using the HeadLace malware, Russian hackers have a very clear objective in mind: access to sensitive databases, banking information, and private networks. The widespread deployment of this malware across European networks has made HeadLace cyber threat a top priority for cybersecurity teams.
Unlike standard malware, HeadLace malware operates in a stealthy manner, making it difficult to detect without advanced security measures. Many companies and institutions have already been affected by this Europe cyber attack, highlighting a need for increased vigilance and better security measures. Russian hackers employ sophisticated methods to deploy HeadLace malware, allowing it to bypass security protocols and wreak havoc on private systems.
How Russian Hackers Deploy HeadLace Malware Across Europe
Reports indicate that Russian hackers are utilizing multiple strategies to spread HeadLace malware across Europe. Often, they target individuals through phishing emails, which contain hidden links or malicious attachments. Once the link is clicked, the malware silently installs on the user’s device, granting Russian cyber attacks access to confidential information. Credential harvesting is then performed by intercepting data as users enter their passwords or usernames.
Another deployment method involves exploiting weaknesses in public and private networks. Hackers can penetrate these networks, especially those with limited security measures, to plant HeadLace malware.Experts in cybersecurity warn that as malware targeting Europe grows more complex, organizations must update their security measures. This cybersecurity concern has brought attention to how crucial it is to teach staff members and consumers safe online habits, like spotting phishing efforts and steering clear of dubious downloads. In addition, these Russian cyberattacks may rely on previously hacked systems to propagate malware further, enabling them to reach a large number of victims with little effort.

The Role of Credential Harvesting in the HeadLace Cyber Threat
Credential harvesting is a primary focus of the HeadLace cyber threat. This involves gathering usernames, passwords, and other login information that allow Russian hackers to access confidential accounts. Due to its ability to obtain credentials from a variety of applications, including social media, online banking, and email accounts, the HeadLace malware poses a particular threat. Once these credentials are obtained, they can be used to steal sensitive data, gain more network access, and act as victims. Credential theft puts financial institutions, government agencies, and private citizens alike in Europe at risk of data breaches.
Impact of the Europe Cyber Attack on Businesses and Individuals
The Europe cyber attack involving HeadLace malware has had far-reaching effects, impacting businesses, institutions, and individuals across multiple sectors. Companies have reported losses of sensitive information, while individuals have experienced identity theft and financial losses. The HeadLace cyber threat has exposed gaps in current cybersecurity frameworks, particularly for small to medium-sized businesses that often lack sufficient protection.
Those Russian cyberattacks show how urgently huge institutions need to implement thorough cybersecurity plans. Incidents of identity harvest and information intrusions have disrupted daily operations, affecting consumer confidence and the image of the company. As Russian hackers continue to spread malware targeting Europe, both businesses and individuals face significant risks if they do not adopt advanced security practices.
Preventive Measures Against the HeadLace Cyber Threat
To combat the HeadLace cyber threat, cybersecurity experts recommend implementing various preventive measures to safeguard systems against this Europe cyber attack. One essential step is to improve employee awareness about phishing and credential theft risks. Users can prevent themselves from unintentionally getting HeadLace malware by identifying phishing efforts.
Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) to safeguard accounts is one of the additional security methods. MFA requires users to authenticate themselves using two or more ways, which increases the difficulty of credential harvesting for Russian hackers. Organizations should also conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities that HeadLace malware could exploit.
To protect yourself from malware that targets Europe, you must always keep your firewall and antivirus software updated. Having regular backups also ensures that crucial data can be recovered from an attack without requiring a ransom payment. By combining these methods, individuals and companies can lower the dangers connected to Russian cyberattacks.

How Authorities and Security Institutions Can Help Fight Russian Cyberattacks
Russian hackers working in Eu continue to represent a cybersecurity danger, prompting multinational cybersecurity organization’s and federal authorities to step up their efforts. Agencies are working together to exchange information regarding the most recent strategies employed by Russian cyberattacks, including the workings of the HeadLace virus.
Additionally, the Europe Union has enforced more stringent data privacy laws that mandate businesses to promptly disclose breaches. These rules push businesses to strengthen their safety protocols and warn clients about possible dangers. The EU’s response to the HeadLace cyber threat demonstrates the critical role of the government in ensuring public safety online.
Furthermore, cybersecurity agencies are developing detection tools that identify and mitigate malware targeting Europe. These tools analyze traffic patterns, helping to identify suspicious activities before they lead to credential theft or a European data breach. By coordinating efforts and utilizing advanced technology, governments and cybersecurity agencies are working to reduce the impact of Russian hackers.
Conclusion
The HeadLace cyber threat has demonstrated the serious risks that Russian cyber attacks pose to Europe. The spread of HeadLace malware and its focus on credential theft has exposed critical vulnerabilities in digital security. As Russian hackers persist in targeting sensitive information, it is essential for governments, businesses, and individuals to strengthen cybersecurity measures. Through awareness, advanced security tools, and regulatory support, Europe can reduce the impact of HeadLace malware and protect against future cybersecurity threats.
FAQs
HeadLace malware is a sophisticated malware that targets sensitive information through credential harvesting, primarily used by Russian hackers.
HeadLace malware is part of a major Europe cyber attack that’s causing widespread credential theft and data breaches.
People can utilize two-factor authentication, be on the lookout for phishing scams, and update their security programs on a regular basis.
Governments and cybersecurity agencies are collaborating to track and counter malware targeting Europe and prevent further European data breaches.